Master Rosacea Treatment for Lasting Calmer Skin
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition causing facial redness, breakouts, and visible blood vessels wit…….
Rosacea treatment has emerged as a critical aspect of dermatological care, focusing on managing and alleviating the symptoms of rosacea, a chronic skin condition characterized by redness, inflammation, and small blood vessels near the skin’s surface. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of various aspects related to rosacea treatment, offering valuable insights for healthcare professionals, researchers, and individuals seeking effective management strategies. We will delve into its historical evolution, global impact, economic implications, technological innovations, regulatory framework, challenges, successful case studies, and future prospects, ultimately highlighting the significance of this treatment approach in modern skincare.
Rosacea treatment involves a multifaceted approach aimed at reducing skin redness, controlling inflammation, and minimizing visible blood vessels. It encompasses a range of therapeutic options, including topical medications, laser therapies, intense pulsed light (IPL), and lifestyle modifications. The primary goal is to soothe symptoms, restore skin texture, and prevent further progression of the condition.
Historically, rosacea treatment has evolved significantly over the centuries. Ancient cultures used natural remedies like aloe vera and chamomile for their anti-inflammatory properties. In the 19th century, early dermatologists introduced topical treatments such as sulfur and calamine lotion. The modern era has witnessed the development of advanced therapies, including specialized lasers and targeted pharmaceuticals, revolutionizing the way rosacea is managed.
Rosacea is a globally prevalent condition, affecting millions worldwide. According to recent estimates, approximately 10% of the population in North America, Europe, and Asia suffers from rosacea, making it a significant public health concern. The impact of rosacea treatment extends beyond individual symptoms, as it can significantly influence self-esteem, social interactions, and overall quality of life.
Internationally, there is a growing awareness and demand for effective rosacea treatments. Countries in North America and Western Europe have seen increased investment in dermatological research, leading to the development of cutting-edge therapies. For instance, the United States has become a hub for clinical trials, with many groundbreaking studies conducted at prominent academic institutions. In contrast, emerging markets in Asia and Latin America are witnessing the rise of accessible, community-based skincare clinics offering affordable rosacea treatments.
The global rosacea treatment market is a thriving sector within the broader dermatology industry, estimated to be worth several billion dollars. This market growth can be attributed to rising consumer awareness, changing lifestyles, and an aging population more susceptible to skin conditions like rosacea. According to a 2022 report by Grand View Research, the global rosacea treatment market size was valued at USD 4.5 billion in 2021 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2022 to 2030.
Market dynamics are influenced by various factors, including the availability of over-the-counter (OTC) products versus prescription medications, the cost of treatments, and regional healthcare disparities. High-income regions tend to have more advanced treatment options, while lower-income areas may face challenges in accessing specialized care and affordable medications. This economic aspect highlights the need for accessible and cost-effective rosacea management strategies.
Technology has played a pivotal role in revolutionizing rosacea treatment, offering more precise, effective, and patient-friendly options. Here are some notable advancements:
Laser Therapies: Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) and laser treatments have become cornerstone therapies for rosacea. IPL targets pigmented blood vessels, reducing redness and flushing. Fractionated laser resurfacing can improve skin texture and reduce visible blood vessels. These procedures are non-invasive and provide long-lasting results.
Advanced Topical Treatments: The development of novel topical medications with targeted delivery systems has enhanced treatment outcomes. For example, gel formulations containing high concentrations of metronidazole have shown superior efficacy in reducing inflammation compared to traditional creams. Additionally, modern delivery systems like nano-emulsions and liposomes improve drug penetration, ensuring better absorption of active ingredients.
Digital Dermatology: Telemedicine and digital imaging tools have transformed rosacea diagnosis and monitoring. High-resolution photography and remote consultations enable dermatologists to assess symptoms accurately, even in geographically diverse regions. This technology also facilitates patient education and adherence to treatment plans.
The development and deployment of rosacea treatments are governed by stringent regulatory frameworks aimed at ensuring safety, efficacy, and quality. These regulations vary across jurisdictions but share common goals. For instance, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requires clinical trials for new drug applications, while the European Medicines Agency (EMA) has a similar process for marketing authorization.
Key considerations include:
Drug Approvals: Regulatory bodies assess the safety and efficacy of rosacea treatments through rigorous clinical trials. This process involves preclinical research, animal studies, and human clinical trials at different phases. Once approved, drugs are assigned specific indications and dosage recommendations.
Labeling and Packaging: Rosacea medications must adhere to strict labeling requirements, providing detailed information on active ingredients, potential side effects, and usage instructions. Package inserts and patient information leaflets ensure informed consent and proper medication use.
Post-Market Surveillance: Regulatory agencies monitor the safety and performance of approved treatments through pharmacovigilance programs. This involves collecting and analyzing adverse event reports to identify potential risks and take appropriate action.
Despite significant progress, rosacea treatment faces several challenges and criticisms that require careful consideration and strategic solutions.
Lack of Personalized Treatments: Rosacea is a heterogeneous condition, presenting different subtypes and varying responses to treatments. The one-size-fits-all approach often falls short, leading to suboptimal outcomes for some patients. Developing personalized treatment plans based on individual symptoms, skin type, and genetic predisposition is an ongoing challenge.
Side Effects and Tolerance: Topical medications, especially in high concentrations, may cause irritation, dryness, or allergic reactions. Laser therapies, while effective, carry risks of temporary redness, swelling, and changes in skin pigmentation. Managing these side effects and ensuring patient tolerance are essential aspects of treatment.
Accessibility and Cost: Access to specialized rosacea care remains a concern in many regions, particularly in underserved communities. High costs associated with advanced treatments like lasers and specialized medications can be a significant barrier to effective management. Addressing healthcare disparities and improving insurance coverage for rosacea therapies are crucial steps towards universal access.
The following case studies illustrate the successful application of rosacea treatment, showcasing improved patient outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
Case Study 1: Sarah’s Journey to Clear Skin
Sarah, a 38-year-old marketing professional, struggled with severe rosacea for over a decade. Her symptoms included persistent redness, broken blood vessels, and occasional pustules on her cheeks and nose. After consulting a dermatologist, she was prescribed a combination of topical medications, including a low-concentration metronidazole gel and a gentle cleanser. Additionally, she underwent three sessions of IPL therapy over two months. Sarah’s treatment plan required adherence to daily skin care routines and regular follow-ups. Within six months, her symptoms significantly improved, achieving clear skin that she had not experienced in years. This case highlights the power of a multidisciplinary approach combining topical treatments and light therapy.
Case Study 2: Community-Based Rosacea Management in India
In a rural area of India, a community health clinic implemented a rosacea management program to address the lack of specialized care. Local healthcare workers were trained to recognize rosacea symptoms and provide basic education on skin care. The program offered OTC medications, such as calamine lotion and topical antibiotics, at subsidized rates. Additionally, they organized regular workshops on sun protection and lifestyle modifications. Within a year, they observed a 35% reduction in patients with active rosacea symptoms, leading to improved self-esteem and social interaction within the community. This case study demonstrates the effectiveness of community-based interventions in managing a previously overlooked condition.
The future of rosacea treatment looks promising, with several emerging trends and growth areas shaping its landscape:
Personalized Medicine: The field is moving towards personalized rosacea care, leveraging advances in genomics and precision dermatology. Understanding individual genetic variations and immune responses will enable tailored treatments, improving efficacy and patient satisfaction.
Combining Therapies: Multimodal treatment approaches that combine topical medications, lasers, and lifestyle modifications are gaining traction. This comprehensive approach addresses various aspects of rosacea, offering more robust and sustained results.
Digital Innovations: Digital health technologies will continue to play a pivotal role in rosacea management. Virtual consultations, mobile apps for skin tracking, and artificial intelligence (AI)-driven diagnostic tools enhance accessibility and patient engagement. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, helping dermatologists make more informed decisions.
Focus on Patient Education: There is a growing emphasis on empowering patients with knowledge about their condition and treatment options. Comprehensive education programs, online resources, and support groups contribute to better self-management and improved outcomes.
Rosacea treatment has come a long way since its early days, evolving into a well-defined, evidence-based field. The comprehensive exploration of its various aspects in this article highlights the significant progress made while also revealing areas that demand continued attention. As the global community continues to embrace advanced technologies, personalized medicine, and accessible care, rosacea treatment is poised to make even greater strides.
By addressing economic considerations, technological advancements, regulatory frameworks, and global trends, we can ensure that effective rosacea management reaches those who need it most. The future prospects outlined here offer a glimpse into the exciting possibilities ahead, ultimately leading to improved quality of life for individuals affected by this chronic skin condition.
Q: What are the early signs of rosacea?
A: Early signs often include intermittent redness, mild swelling, and small blood vessels visible just beneath the skin’s surface. It may also present with a sensation of warmth or burning in affected areas.
Q: Can rosacea be cured? Is it lifelong?
A: Rosacea is a chronic condition, meaning it cannot be entirely cured. However, with proper management, symptoms can be significantly reduced and controlled for many years. Flare-ups can occur periodically, but effective treatment plans help minimize their frequency and severity.
Q: Are there any natural remedies for rosacea?
A: While some natural remedies may provide temporary relief, they are generally not considered as effective as prescribed medications or professional treatments. Aloe vera, green tea, and certain herbal supplements have shown some promise in preliminary studies, but more research is needed. Always consult a dermatologist before trying alternative therapies.
Q: How often should I see a dermatologist for rosacea?
A: The frequency of visits depends on the severity of your condition and response to treatment. Initially, weekly or bi-weekly consultations may be necessary to monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan. Once symptoms are under control, visits can be reduced to every few months.
Q: Are laser treatments painful for rosacea?
A: Laser therapies for rosacea are generally well-tolerated, but discomfort is expected. Modern lasers use cooling mechanisms to minimize pain, and most patients report only mild discomfort during the procedure. Post-treatment redness and swelling are temporary.
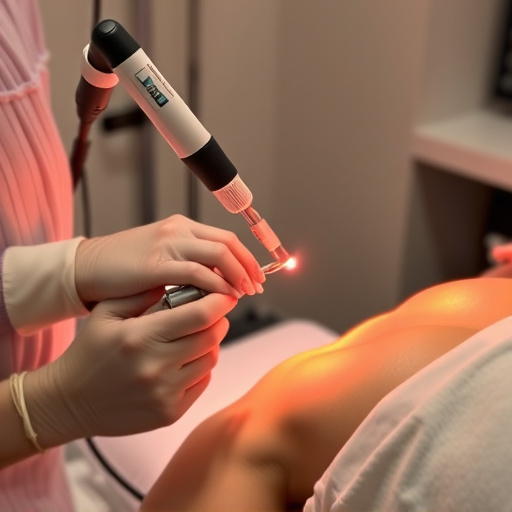
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition causing facial redness, breakouts, and visible blood vessels wit…….
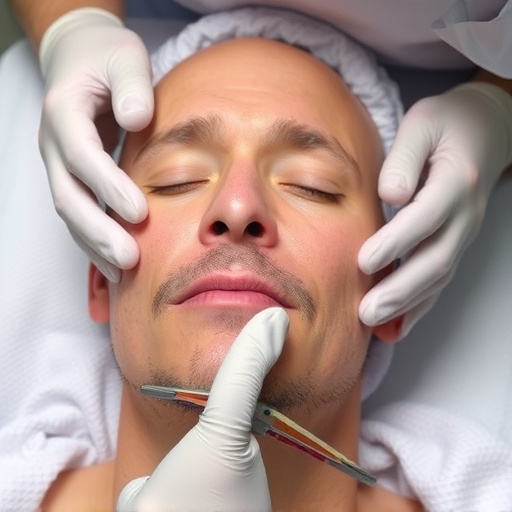
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition with unknown cause, characterized by redness, bumps, and flushin…….
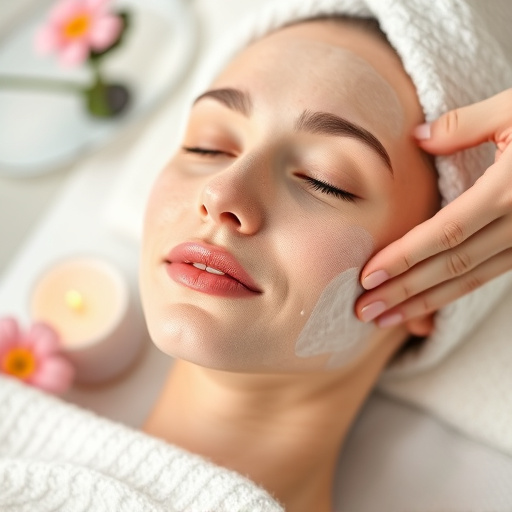

Rosacea is a chronic skin condition with no cure, requiring professional rosacea treatment plans inc…….